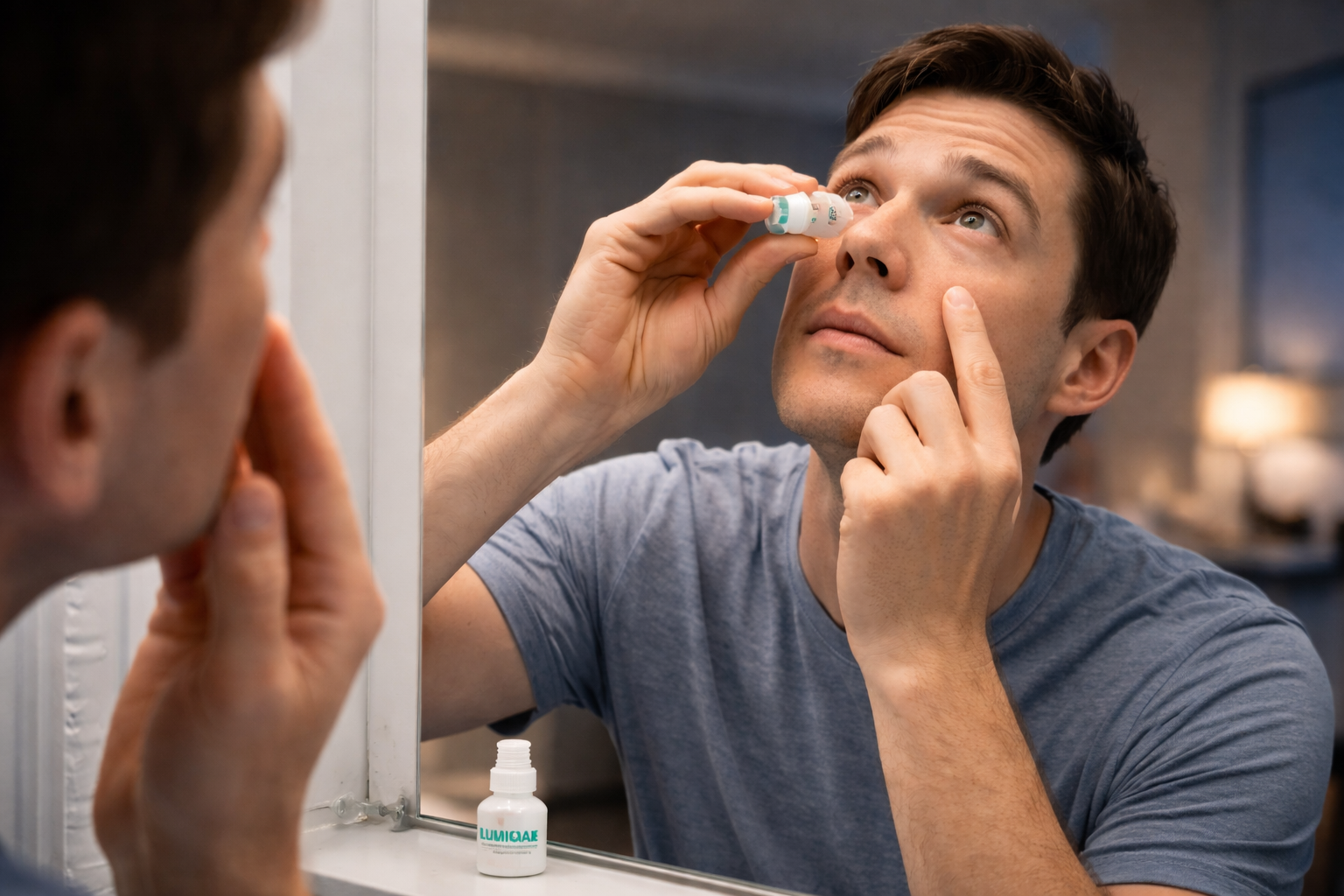
Why is Lumigan Taken at Night?
Why is Lumigan Taken at Night? Lumigan (bimatoprost) is usually taken at night because the drops are meant to be used once daily and can cause brief blurred vision or redness right after they are applied. Using the drops before bed allows the medicine to start lowering eye pressure while you sleep, and it also avoids those temporary effects interfering with daytime activities. A lot of patients hear this instruction and immediately wonder why Lumigan is taken at night instead of in the morning. It’s a reasonable question. After all, many medications can be taken at any time of day. With Lumigan, though, evening use simply tends to work better for most people. Part of the reason is how the medicine works. Another part is just practical — it’s easier to deal with temporary eye irritation when you’re already getting ready for sleep. Why Evening Use Is Recommended for Lumigan Lumigan is designed to be used once per day. Not twice, not several times throughout the day — just once. Because of that, doctors usually suggest picking a time that’s easy to stick with. Evening works well for many people. It naturally becomes part of a bedtime routine. There’s also another practical reason. Right after putting the drops in, some people notice their vision looks slightly blurry for a short time. The eyes might feel a little irritated or red too. It doesn’t last very long, but it can be annoying if it happens during the day while you're working, reading, or driving. Using the medication in the evening avoids that problem. By the time morning comes, the temporary effects are usually gone. That’s why doctors often recommend Lumigan eye drops night use when explaining the treatment schedule. How Lumigan Helps Control Eye Pressure Overnight Lumigan belongs to a group of medications called prostaglandin analogs. These medicines work in a specific way inside the eye. The eye naturally produces a clear fluid. That fluid constantly drains out through small pathways. When the drainage doesn’t work properly, pressure inside the eye begins to build. This pressure is what doctors worry about in conditions like glaucoma. Over time, high pressure can slowly damage the optic nerve — the nerve that sends visual signals from the eye to the brain. Once that nerve is damaged, vision loss can occur. Lumigan helps solve that problem by improving how fluid drains from the eye. The medication increases the natural outflow of fluid, which lowers the pressure. Using the drops before bed allows the medication to start working overnight. That steady pressure reduction helps protect the optic nerve over time. For people with glaucoma, maintaining that stable pressure is extremely important. What Happens If Lumigan Is Used During the Day Some patients ask a simple question: Can Lumigan be used in the morning instead? Technically, yes. The medication will still work if it’s taken during the day. But there are a few reasons doctors usually prefer evening use. The first is convenience. As mentioned earlier, temporary blurred vision can occur right after applying the drops. If that happens in the middle of the day, it may interfere with things like reading, driving, or working on a computer. Another issue is that mild redness or irritation can appear shortly after the drops are used. While this usually fades fairly quickly, it can feel more noticeable when you’re going about your daily routine. Because of this, nighttime tends to be the best time to use Lumigan eye drops for many patients. That said, the most important factor is consistency. Using the drops at the same time every day matters more than the exact hour. Why Using Lumigan More Than Once a Day Is Not Recommended It might seem logical to assume that using the drops more often would lower eye pressure faster. But Lumigan doesn’t work that way. In fact, using the medication more than once daily can actually make it less effective. Prostaglandin analog medications reach their best effect when used once per day. Using them too frequently may reduce their pressure-lowering ability. It can also increase side effects such as: eye redness• irritation• dryness• sensitivity For this reason, doctors usually recommend a simple schedule:one drop in the affected eye once each evening. If a dose is missed occasionally, it’s generally best to just continue with the next scheduled dose rather than doubling up. Tips for Using Lumigan Correctly at Night Using eye drops properly makes a difference. Small steps can help the medication work more effectively and prevent contamination. Here are a few helpful tips for using Lumigan at night. First, wash your hands before handling the bottle. If you wear contact lenses, remove them before applying the drops. Most doctors recommend waiting about 15 minutes before putting lenses back in. Tilt your head back slightly and gently pull down the lower eyelid. Then place one drop in the eye as directed. Try not to let the dropper tip touch your eye or skin. That helps keep the bottle clean. Many patients find it easier to remember their drops when they connect them with another nightly habit, like brushing their teeth. Pharmacists at Grant Pharmacy often help patients review these instructions, especially if someone is new to using glaucoma eye drops. Possible Side Effects to Be Aware Of Most people tolerate Lumigan quite well, but side effects can happen. Some of the more common ones include: mild eye redness• temporary blurred vision after using the drops• slight irritation or dryness• increased eyelash growth Another effect that sometimes occurs over time is a gradual darkening of the iris, the colored part of the eye. This doesn’t happen to everyone, but it’s something doctors usually mention before starting treatment. Most of these effects are mild. Still, if symptoms become bothersome or persistent, it’s a good idea to discuss them with a healthcare provider. When to Speak With Your Eye Doctor People using glaucoma medications should stay in regular contact with their eye doctor. You should contact your doctor if you notice things like: severe eye redness or pain• sudden vision changes• swelling around the eye• allergic reactions• frequent missed doses Doctors may also want to check eye pressure periodically to make sure the medication is working as expected. Sometimes patients are prescribed more than one glaucoma medication. In those situations, doctors may give instructions about spacing different eye drops during the day. Accessing Lumigan Through a Trusted Pharmacy Managing glaucoma treatment often involves more than just taking the medication. Patients may have questions about dosing schedules, side effects, or how the drops should be stored. People who want to learn more about eye medications or prescription support can explore information available at grantpharmacy.com, where educational resources on eye care and medication guidance are available. Using Lumigan consistently — and understanding why Lumigan should be used at night — can help patients maintain better control of eye pressure and protect their long-term vision.













.png)
.jpg)